Imagine walking through a building as it's being designed, experiencing the interplay of light, space, and materials in real time. No printed blueprints, no static 3D renderings on a screen, just a fully immersive exploration of your architectural vision before the first brick is laid. Virtual Reality (VR) has made this a reality, and it is revolutionizing how we think about architectural design.
Gone are the days when collaboration meant sitting around a conference table with 2D plan sets and 3D renderings. VR platforms for real-time architectural co-design are ushering in a new era of creativity and precision. By leveraging immersive environments, these tools enable architects, clients, and stakeholders to collaborate, experiment, and refine designs in ways never before possible.
This article explores how VR is transforming architectural co-design, highlights leading platforms in the space, and sheds light on why this technology is becoming a game-changer for the industry.
The Benefits of VR in Architectural Co-Design
Why is VR such a powerful tool for architectural collaboration? The answer lies in its unique ability to enhance communication, streamline workflows, and minimize costly errors.
1. Real-Time Collaboration Across Teams and Locations
One of the most significant advantages of VR is its ability to bring people together, no matter where they are physically located. Picture an architect in Los Angeles, a client in London, and an engineer in Tokyo, all walking through the same virtual model simultaneously.
VR platforms allow team members to annotate designs, make adjustments, and discuss ideas as if they’re in the same room. This eliminates communication bottlenecks and fosters a deeper understanding of the project for everyone involved.
2. Enhanced Visualization and Perspective
While 3D renderings and CAD models are useful, they have limitations. On a flat screen, it’s difficult to fully grasp how a space will feel. VR solves this by placing users directly inside the design.
Want to experience how morning sunlight will stream into a living room? Curious whether the lobby ceiling feels too low? VR ensures these questions can be answered before construction begins. This improved visualization not only aids architects but also helps clients envision spaces more clearly, leading to better-informed decisions.
3. Improved Feedback Loops
Traditionally, design iterations can take weeks as architects and clients exchange emails, plans, and comments. VR drastically shortens this timeline. Multiple stakeholders can evaluate and adjust designs in real time, allowing for immediate feedback and rapid refinement.
Interactive elements, such as adjusting materials, light sources, or furniture layouts on the fly, further streamline the co-design process. This speed and agility reduce the risk of miscommunication and ensure that everyone shares an aligned vision.
4. Cost Efficiency
Mistakes in architecture are often expensive, especially when discovered during or after construction. VR mitigates this risk by enabling more accurate planning and testing in the design phase.
For example, clients might realize that an open-plan office concept feels less practical in VR than it did on paper. Catching such issues early avoids costly redesigns later. Additionally, VR models often reduce the need for physical prototypes, saving both time and money.
Leading VR Platforms for Architectural Co-Design
The explosion of interest in VR has resulted in a wide variety of platforms tailored to architecture and design professionals. Each offers unique features that cater to different workflows and needs. Here are some of the leading players transforming the industry:
1. Unity Reflect
Unity Reflect bridges the gap between BIM (Building Information Modeling) and VR. By integrating directly with Revit, it allows architects to turn BIM models into immersive VR experiences with just a few clicks.
- Key Features:
- Real-time updates: Any changes made in Revit are reflected immediately in the VR environment.
- Multiuser collaboration tools for real-time co-design.
- Accessibility across devices, including VR headsets, tablets, and desktops.
Unity Reflect is particularly valued for its ability to seamlessly incorporate real-time data visualization into its immersive models.
2. Enscape
Enscape is known for its simplicity and speed. It integrates with popular design tools like SketchUp, Rhino, Archicad, and Revit, enabling instant VR experiences without the need for complex export processes.
- Key Features:
- One-click VR walkthrough generation.
- Stunning visual fidelity, including realistic lighting and material rendering.
- Integrated collaboration features like annotations and screenshots.
Because of its user-friendly design, Enscape is a favorite among firms aiming to simplify presentations and boost client engagement.
3. Arkio
Designed specifically for real-time collaboration, Arkio allows architects and clients to sculpt and tweak designs collaboratively in VR. It’s a versatile platform that works with most devices—even mobile ones.
- Key Features:
- Intuitive modeling tools for real-time creation and editing.
- Multiuser sessions, bringing teams and stakeholders together.
- Integration with existing workflows through export options for Revit and Rhino.
Arkio is particularly effective in early design phases, when creativity and iteration are key.
4. IrisVR Prospect
Targeted at architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals, IrisVR Prospect emphasizes immersive design review and collaboration.
- Key Features:
- Compatibility with BIM and CAD software like Revit, SketchUp, and Navisworks.
- The ability to simulate true-to-life scale, making spatial understanding seamless.
- Multiuser virtual meetings for client reviews or team discussions.
For complex projects requiring detailed review, IrisVR Prospect shines as a collaborative powerhouse.
How VR is Reshaping the Architecture Industry
The integration of VR into architectural co-design marks a shift from static, isolated workflows to dynamic, collaborative ones. It is not simply a tool for visualization; it’s a platform for innovation and exploration. Here’s how it’s transforming the industry:
1. Making Design More Accessible
Clients without architectural or engineering backgrounds often struggle to interpret 2D plans or even 3D renderings. VR takes the guesswork out of the equation by allowing clients to experience designs from a first-person perspective. This empowers them to provide more meaningful input, leading to designs that better meet their needs.
2. Enhancing Sustainability
VR enables architects to test sustainable solutions in a virtual space before implementing them in the real world. For example, they can evaluate how natural light usage reduces energy requirements or test environmentally friendly materials within the context of the entire design.
3. Facilitating Remote Work
The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped the way we work, and VR has since emerged as a critical tool for remote collaboration. By allowing dispersed teams to work together as if they’re in the same room, VR platforms have helped architecture firms maintain productivity and creativity in challenging circumstances.
4. Expanding Possibilities for Customization
VR empowers designers to test endless variations of a design without significant time or resource investment. Want to explore how a different layout affects flow? Or compare brick and stucco facades? VR makes this process seamless.
What’s Next for VR in Architecture?
The line between the digital and physical world is continuing to blur. Emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) promise even greater integration of virtual tools into architectural workflows. Imagine overlaying VR designs onto construction sites in real time, enabling even more precise execution of plans.
Additionally, advancements in hardware, such as lightweight headsets and 3D interface tools, will likely make VR even more accessible to smaller firms and solo practitioners.
VR platforms are transforming architectural co-design by unlocking new levels of collaboration, creativity, and precision. From allowing clients to experience their projects before they’re built to speeding up feedback loops, the benefits are undeniable.
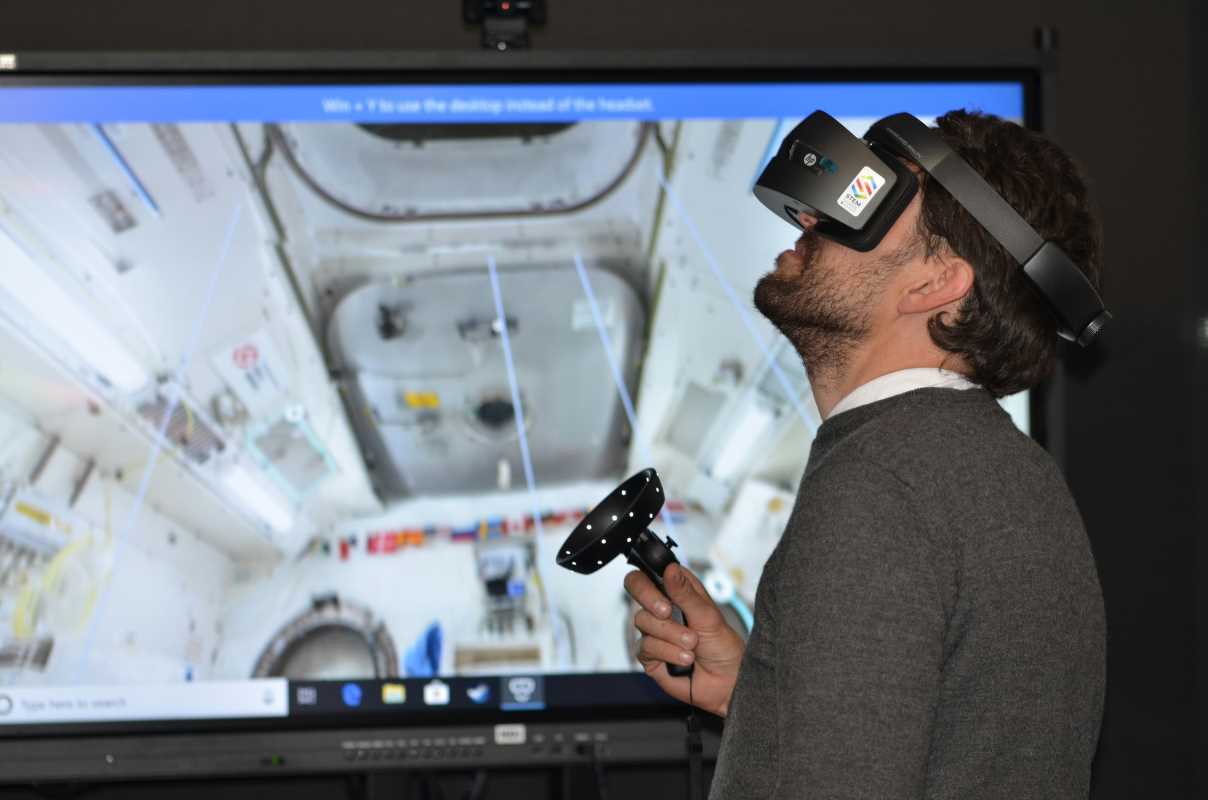 (Image via
(Image via